Disclaimer
The use of commands is at your own risk. Never use commands unless you fully understand their functionality.
CMD Commands do work in Powershell in most cases (but not vice-versa) to add several commands in a single execution, in PS use ‘;’ in CMD use ‘&’
General Windows Info
Windows Version
Get-CimInstance Win32_OperatingSystem | Select-Object Caption, Versionsysteminfo | findstr /B /C:"OS Name" /B /C:"OS Version"last bootup-Time
Get-CimInstance -ClassName Win32_OperatingSystem | Select-Object LastBootUpTimesysteminfo | find "System Boot Time"Get Last Shutdown/Reboot Events
fetches shutdown/reboot events from Eventlogger
Get-EventLog -LogName system -Source user32 | Select TimeGenerated, Message -Unique | ft -WrapPending Reboot
Install Module
Install-Module -Name PendingReboot
Import-Module PendingRebootRun CMDLet:
Test-PendingReboot -DetailedDisplay Device Domain Join Status
dsregcmd /statusGet Device-Certificate Expiration-Date
only works if Certificate Name contains the devices hostname
Get-ChildItem Cert:\LocalMachine\My |
Where-Object { $_.Subject -match $(hostname) } |
Select-Object Subject, Thumbprint, NotAfterSet/Change System Environment Variable
(requires reboot afterwards)
$vName = Read-Host "Name"
$vValue= Read-Host "Value"
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Session Manager\Environment" -Name $vName -Value $vValueBattery Report
powercfg /batteryreportget hotfix Info
Get-HotFix | Select-Object -First 20 -Property Description, HotFixID, InstalledOn | Sort-Object -Property InstalledOn -Descendingwmic qfe list brief /format:table | findstr /i /v "Caption"Advanced query using Microsoft.Update.Session Searcher:
$Session = New-Object -ComObject "Microsoft.Update.Session"
$Searcher = $Session.CreateUpdateSearcher()
$historyCount = $Searcher.GetTotalHistoryCount()
if ($historyCount -le 0) {
Write-Warning "No Windows Update history available."
return
}
$Searcher.QueryHistory(0, $historyCount) |
Select-Object Date, Title,
@{Name="KB"; Expression={
if ($_.Title -match "KB\d+") { $matches[0] } else { "" }
}},
@{Name="Category"; Expression={
$t = $_.Title
switch -Regex ($t) {
"Kumulatives Update für Windows|Cumulative Update for Windows|Windows-Tool zum Entfernen bösartiger Software|Windows Malicious Software" { "OS patch" }
"\.NET|NET Framework" { ".NET" }
"Firmware|UEFI|BIOS" { "Firmware" }
"Treiber|Driver|Intel|NVIDIA|AMD|Realtek" { "Driver" }
"^9[A-Z0-9]{11}-" { "Store app / MSIX" }
"VCLibs|DesktopAppInstaller|NET.Native" { "MSIX framework" }
default { "Other" }
}
}},
@{Name="Operation"; Expression={
switch ($_.Operation) {
1 {"Installation"}
2 {"Uninstallation"}
3 {"Other"}
}
}},
@{Name="Result"; Expression={
$rc= $_.ResultCode
$hr = $_.HResult
$text = switch ($rc) {
0 { "Not started ($rc)" }
1 { "In progress ($rc)" }
2 { "Succeeded ($rc)" }
3 { "Succeeded with errors ($rc)" }
4 { "Failed ($rc)" }
5 { "Aborted ($rc)" }
default { "Unknown ($rc)" }
}
if ($rc -eq 4 -and $hr -ne 0) {
"$text [$( '0x{0:X8}' -f ($hr -band 0xFFFFFFFF) )]"
} else {
$text
}
}},
Description
Shutdown
shutdown PC after the time given with /t xxx (in seconds)
for reboot add /r
the /f Flag enforces the shutdown… loged in users get signed out!
on execution, active users get a notification that the PC will shutdown in t time, without further notice
shutdown /f /t 0CPU Info
CPU – Overall Usage
returns a single value of the total average usage
Get-CimInstance win32_processor | Measure-Object -Property LoadPercentage -AverageCPU – Overall Usage (continuous)
Returns a single value of the total average usage
While($true){
Get-CimInstance win32_processor | Measure-Object -Property LoadPercentage -Average | Select-Object Average
Start-Sleep -Seconds 1
} CPU – High usage processes
Get processes using the most CPU (using logical processes… values over 100% possible)
-gt 2 = more than 2 seconds of CPU time
(Get-Counter '\Process(*)\% Processor Time').CounterSamples | Where-Object {$_.CookedValue -gt 2} | Select-Object -Property InstanceName, CookedValue | Sort-Object -Property cookedvalue -DescendingWindows System
Bypass Execution Policy
Allow temporary Script-Execution
set-executionpolicy bypassWindows Troubleshooter (old, GUI)
Win11: Microsoft moves Troubleshooter to their “Get Help” app.
Currently, most Troubleshooters known until Windows 10 are still available in Win11 23H2 using msdt.exe
For a list of available packages, see Available Troubleshooting packs.
Example: Run Network Adapter Diagnostics:
msdt.exe /id NetworkDiagnosticsNetworkAdapterWindows Troubleshooter (Powershell cmdlet, unattended)
Get-TroubleshootingPack -Path C:\Windows\diagnostics\system\WindowsUpdate | Invoke-TroubleshootingPack -UnattendedOther Diagnostic-Paths:
| Diagnostics Pack | Directory |
|---|---|
| Apps | C:\Windows\Diagnostics\System\Apps |
| Audio | C:\Windows\Diagnostics\System\Audio |
| BITS (Background Intelligent Transfer Service) | C:\Windows\Diagnostics\System\BITS |
| Bluetooth | C:\Windows\Diagnostics\System\Bluetooth |
| Device (Hardware and Devices Troubleshooter) | C:\Windows\Diagnostics\System\Device |
| DeviceCenter (specific Devices, requires Device Container ID) | C:\Windows\Diagnostics\System\DeviceCenter |
| IEBrowseWeb | C:\Windows\Diagnostics\System\IEBrowseWeb |
| IESecurity | C:\Windows\Diagnostics\System\IESecurity |
| Keyboard | C:\Windows\Diagnostics\System\Keyboard |
| Networking | C:\Windows\Diagnostics\System\Networking |
| Program Compatibility Wizard | C:\Windows\Diagnostics\System\PCW |
| Power | C:\Windows\Diagnostics\System\Power |
| Printer | C:\Windows\Diagnostics\System\Printer |
| Search | C:\Windows\Diagnostics\System\Search |
| Speech | C:\Windows\Diagnostics\System\Speech |
| Video | C:\Windows\Diagnostics\System\Video |
| WindowsMediaPlayerConfiguration | C:\Windows\Diagnostics\System\WindowsMediaPlayerConfiguration |
| WindowsMediaPlayerMediaLibrary | C:\Windows\Diagnostics\System\WindowsMediaPlayerMediaLibrary |
| WindowsMediaPlayerPlayDVD | C:\Windows\Diagnostics\System\WindowsMediaPlayerPlayDVD |
| WindowsUpdate | C:\Windows\Diagnostics\System\WindowsUpdate |
General System Repair
System-Files & Component Store Repair
(PowerShell command notifies the user after completion)
$(
Start-Process DISM.exe -Wait -NoNewWindow -ArgumentList "/Online /Cleanup-image /Scanhealth"
Start-Process DISM.exe -Wait -NoNewWindow -ArgumentList "/Online /Cleanup-image /RestoreHealth"
Start-Process SFC.exe -Wait -NoNewWindow -ArgumentList "/scannow"
# Notify the user
Add-Type -AssemblyName System.Windows.Forms
Add-Type -AssemblyName System.Drawing
$msg="Please Restart your Device using the 'Restart' option."
$notification = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.NotifyIcon
$notification.Icon = [System.Drawing.SystemIcons]::Information
$notification.BalloonTipTitle = "Windows System Repair"
$notification.BalloonTipText = $msg
$notification.Visible = $true
$notification.ShowBalloonTip(30000)
# Activate the PS Window to notify the user
Add-Type -AssemblyName Microsoft.VisualBasic
[Microsoft.VisualBasic.Interaction]::AppActivate($PID)
Write-Host "`r`nSystem-Repair completed" -ForegroundColor Green
Write-Host $msg
Pause ; exit
)DISM.exe /Online /Cleanup-image /Scanhealth
DISM.exe /Online /Cleanup-image /RestoreHealth
sfc /scannowComponent Store Cleanup
if /RestoreHealth results in an error that the source files can not be found, this may sometimes resolve the issue
DISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /AnalyzeComponentStoreif /AnalyzeComponentStore results in the information that a Component Store Cleanup is advised, proceed with the following
DISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /StartComponentCleanupMemory Repair
Each (Efficiency)CPU core can scan 4 GB in parallel in about 20 minutes (limited by RAM/DDR speed limits)
e.g. 4-core CPU scans 16 GB in 20 min, 2-core CPU scans 16 GB in 40 min, 8-core CPU scans 16 GB in 20 min as well
MDSCHEDDisk Check and repair
- /r: This switch tells CHKDSK to locate bad sectors in the disk and attempt to recover any readable information from them. It also implies the functionality of /f, so you don’t need to specify /f separately.
- /f: This switch tells CHKDSK to fix any errors it finds on the disk.
chkdsk /r /fSpecific System Repair
Reset Explorer Views
force resets all Explorer view Settings
Delete the following keys and restart Explorer
HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\Shell\Bags
HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\Shell\BagMRURepair WMI repository
winmgmt /verifyrepository
winmgmt /salvagerepository
stop-service -force winmgmt
start-service winmgmtRepair All AppxPackages
Repair all Packages and system modules
remove -AllUsers to only repair the modules for the current user (Users may have separate modules from -AllUsers)
Get-AppxPackage -AllUsers | ForEach-Object {
Add-AppxPackage -DisableDevelopmentMode -Register "$($_.InstallLocation)\AppXManifest.xml"
}Further information can be found here: MS Store & Winget: App-Management in Windows
Repair Specific AppxPackages
Repair a specific Module (such as DesktopAppInstaller/Winget)
remove -AllUsers to only repair the modules for the current user (Users may have separate modules from -AllUsers). Change -Name if needed for a different module.
Get-AppxPackage -Name Microsoft.DesktopAppInstaller -AllUsers | ForEach-Object {
Add-AppxPackage -DisableDevelopmentMode -Register "$($_.InstallLocation)\AppXManifest.xml"
}Other AppxPackages:
Further information can be found here: Windows Explorer: A Powerhouse for it all
Microsoft.Windows.ShellExperienceHost→ Handles the Taskbar, Start Menu, and other shell components.Microsoft.Windows.Taskbar(on newer builds) → Manages specific Taskbar-related functionality.Microsoft.Windows.ActionCenter→ Controls the notification area (Action Center), a part of the Taskbar.Microsoft.Windows.StartMenuExperienceHost→ Responsible for rendering the Start Menu UI.Microsoft.Windows.Photos→ Windows Photos ApplicationMicrosoft.BingSearch-> responsible for the Web-Search integration in Windows Search (such as Taskbar Search or Startmenu)
General Windows Update Troubleshoot
Windows-Update Troubleshooter (old)
msdt.exe /id WindowsUpdateDiagnosticWindows-Update Troubleshooter (cmdlet)
Get-TroubleshootingPack -Path C:\Windows\diagnostics\system\WindowsUpdate | Invoke-TroubleshootingPack -Unattended
Get-TroubleshootingPack -Path C:\Windows\diagnostics\system\BITS | Invoke-TroubleshootingPack -UnattendedReset WUA & BITS Services
$currentDateTime=(Get-Date).ToString("yyyy-MM-dd_HH-mm")
$softwareDistributionPath = "$Env:systemroot\SoftwareDistribution"
$catroot2Path = "$Env:systemroot\system32\catroot2"
$softwareDistributionBackupPath = "$softwareDistributionPath.bak"
$catroot2BackupPath = "$catroot2Path.bak"
$Services = 'msiserver','trustedinstaller','ccmexec','wuauserv','bits','appidsvc','cryptsvc','smstsmgr'
Get-Process 'msiserver','trustedinstaller','ccmexec' -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue | Stop-Process -Force
Get-Service $Services -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue | Stop-Service -Force
if (Test-Path -Path $softwareDistributionBackupPath) {
Write-Verbose "Backup directory exists. Deleting $softwareDistributionBackupPath..."
Remove-Item -Path "\\?\$softwareDistributionBackupPath" -Recurse -Force -Verbose
}
if (Test-Path -Path $softwareDistributionPath) {
Rename-Item -Path "\\?\$softwareDistributionPath" -NewName SoftwareDistribution.bak
}
if (Test-Path -Path $catroot2BackupPath) {
Write-Verbose "Backup directory exists. Deleting $catroot2BackupPath..."
Remove-Item -Path "\\?\$catroot2BackupPath" -Recurse -Force -Verbose
}
if (Test-Path -Path $catroot2Path) {
Rename-Item -Path "\\?\$catroot2Path" -NewName catroot2.bak
}
Get-Service $Services -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue | Start-Service
$successMessage = "Windows Update Cleanup successfully.`r`nSoftwareDistribution and catroot2 folders have been renamed."
Write-Host "`r`n`r`n[$currentDateTime] - INFO:`r`n$successMessage"net stop bits
net stop wuauserv
net stop cryptsvc
net stop appidsvc
net stop msiserver
net stop trustedinstaller
net stop ccmexec
net stop smstsmgr
rmdir %systemroot%\SoftwareDistribution /S /Q
rmdir %systemroot%\system32\catroot2 /S /Q
net start cryptsvc
net start wuauserv
net start bits
net start appidsvc
net start msiserver
net start trustedinstaller
net start ccmexec
net start smstsmgr Windows Update Install (PowerShell)
install module
Install-PackageProvider -Name NuGet -MinimumVersion 2.8.5.201 -Force
Install-Module -Name PSWindowsUpdate -Force
Get-Package -Name PSWindowsUpdate
Import-Module PSWindowsUpdateinstall Update
(switch -KBArticleID to -updateID to use Windows update Catalog UpdateID instead of KB-number)
Get-WindowsUpdate -Install -KBArticleID KB5017308Network-Drive Mapping Fix
Windows tries to map the network drives immediately when loading the Profile, even if no network is available… This may cause the Drives not to be available in the Explorer.
As prevention, run gpedit and enable the policy: “Always wait for the network at computer startup and logon” located under Computer Configuration -> Policies -> Administrative Templates -> System -> Logon
Restart the Services:
Stop-Service @('FDResPub','fdPHost')
Start-Service @('fdPHost','FDResPub')Restart Printer Spooler
restart-service spoolernet stop spooler
net start spoolerEnable Win32 Long Paths
Enable the use of long File-Paths (usually max 260, long-path max: 32.767)
New-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\FileSystem" -Name "LongPathsEnabled" -Value 1 -PropertyType DWORD -ForceReset Logon Cache
e.g. if running sfc /scannow as admin states that you need to be Admin
- as Administrator, open Local Security Policy (secpol.msc)
- navigate to: Local Policies > Security Options > search for Interactive logon: Number of previous logons to cache (in case domain controller is not available)
- change value to 0
- sign out & back in
- Change back to 10
- Sign out & back in
Check User Sessions
get logged in users on machine
query userlog off specific session (replace <ID> from command-result above)
logoff <ID>long Shutdown Fix
- Win Settings > Updates > Troubleshoot > additional troubleshooters > Power
- Turn off fast boot via Control Panel -> Power Options -> Choose what the Power buttons do
- turn off clearing PageFile on shutdown by changing ClearPageFileAtShutdown to 0 :
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Session Manager\Memory Management- change WaitToKillServiceTimeout to 2000 (or higher)
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\ControlSoftware Uninstallation
Uninstallation troubleshooter:
To troubleshoot failing installs and un-installs, Microsoft provides a specific Troubleshooter:
Simply download via this direct-Link, or via support.microsoft.com.
Get all installed Software (via WMI)
Get-WmiObject -Class Win32_Product | select Name, Version, Vendor | Sort-Object -Property NameSearch installed Software-Packages
$str = Read-Host "Enter Package-Name (Part)"
Get-Package | Where-Object { $_.Name -match "$str" }remove installed Software (via WMI)
use Full name provided by the Get all installed Software section above
$pkgName = Read-Host "Enter the Package Name"
(Get-WmiObject -Class Win32_Product | Where-Object{$_.Name -eq "$pkgName"}).Uninstall()remove installed Software-Package
use Full name provided by the Search installed Software-Packages section above
$pkgName = Read-Host "Enter the Package Name"
Uninstall-Package -Name $pkgName -ConfirmBulk Uninstall
Dangerous!
Uninstall All Packages from a Specific Vendor:
Github (halatsWol): bulkUninstall.ps1
Microsoft Support and Recovery Assistant (cmd-based)
(OffScrub)
Removes all MS Office installations and Residuals
Download Assistant from: https://aka.ms/SaRA_EnterpriseVersionFiles
Documentation: https://aka.ms/SaRA_CommandLineVersion
- Download Assistant
- Extract the files (e.g. to C:\Temp\)
- Open CMD as Admin
- Change to the directory where the files are located (e.g. ” cd ‘C:\Temp\SaRACmd_17_01_2276_000\’ “)
- Run the following command:
SaRAcmd.exe -S OfficeScrubScenario -AcceptEula -OfficeVersion AllAutodesk Clean-Uninstall
Manual uninstall – Autodesk Documentation: How to perform a Clean Uninstall of Autodesk products on Windows
Automated Uninstall:
Download the Script from Github: AutoDeskCleanRemove.ps1
(e.g. move to C:\Temp\ )
or directly download it into the Temp Folder using Powershell:
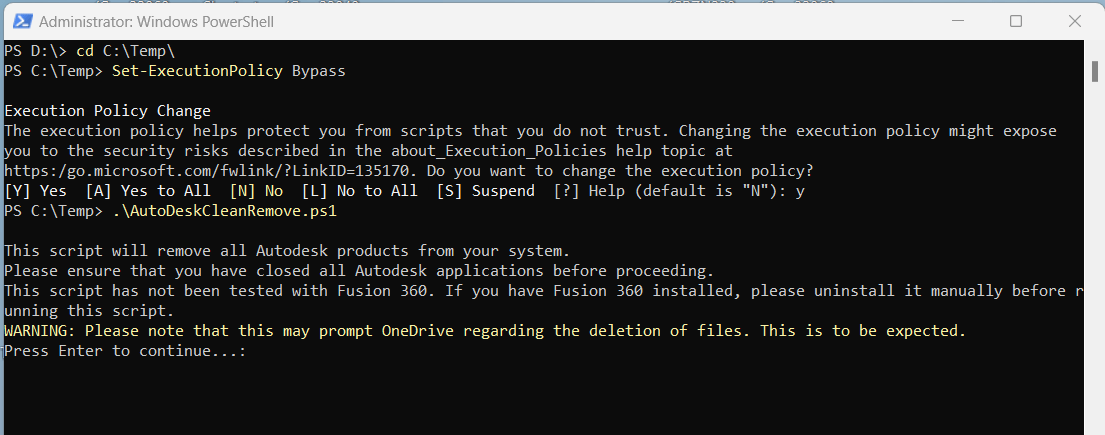
Invoke-WebRequest -Uri "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/halatsWol/PowerShell-Tools/main/scripts/AutoDeskCleanRemove.ps1" -OutFile "C:\Temp\AutoDeskCleanRemove.ps1"- open Powershell as Administrator
- Navigate to the Folder where the Script is located using
cd C:\Temp\ - (optional) bypass Script-Execution (confirm with ‘Y’):
Set-ExecutionPolicy Bypass- Execute the Script
.\AutoDeskCleanRemove.ps1- Continue with [Enter] after reading the initial Informations,
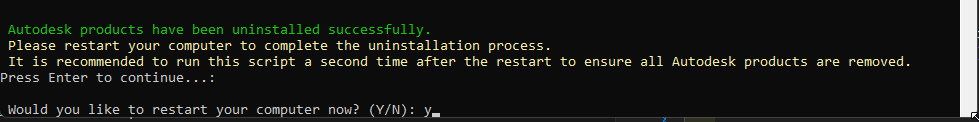
The Script will now start to uninstall all Autodesk Products (duration ~20-30min depending on amount of installed Products)
Uninstallation will delete items from Documents & Pictures Folder ( example files and projects ) … this may cause OneDrive to throw a Warning >> simply accept the file-deletion
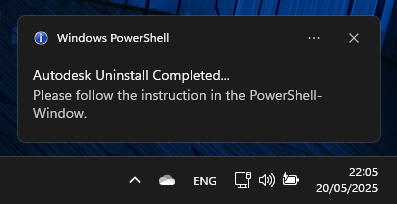
- Once the removal has completed, the user will be notified (Windows Notification)

- Follow the instruction in the PowerShell Window to Restart the Device and repeat the steps 2-8 (Process will only need a few minutes)

General Software Repair
Office
Office 365 General
Office File Cache
Office File Cache is used to store files that are used by Office Applications. If office does not work properly these file will not be cleared when Closing the Office-Document. This may cause “File in use” issues
clear Cache via Office > File > Options > Save > Cache Settings > Delete Cached Files. Doubble check the path below if it is empty
Additionally set in Office > File > Options > Save > Cache Settings > Delete files from the Office Document Cache when they are closed
Cache Location:
%LOCALAPPDATA%\Microsoft\Office\16.0\OfficeFileCacheOffice repair
Start-Process -FilePath "$env:ProgramFiles\Microsoft Office 15\ClientX64\OfficeClickToRun.exe"`
-ArgumentList "scenario=Repair", "platform=x64", "culture=en-us", 'DisplayLevel=False' -Waitcd "%ProgramFiles%\Microsoft Office 15\ClientX64\"
OfficeClickToRun.exe scenario=Repair platform=x64 culture=en-us DisplayLevel=FalseOffice x86 to x64 upgrade
When upgrading Microsoft Office 365 from x86 to x64 Architecture, it may happen that a Registry Entry is not removed which points to the Program Files x86 Path.
This may cause 3rd Party Software which communicates with MS Office to throw Errors
$regPath = 'HKLM:\Software\Classes\TypeLib\{00062FFF-0000-0000-C000-000000000046}\9.6\0\Win32'
if (Test-Path $regPath) {
try {
Remove-Item -Path $regPath -Recurse -Force
Write-Host 'The "Win32" folder has been successfully deleted from the registry.'
} catch {
Write-Host 'An error occurred while trying to delete the "Win32" folder: $_'
}
} else {
Write-Host 'The WWin32W folder does not exist in the specified registry path.'
}Office update (cmd/PS)
to update MS Office via Shell using the Click to Run Client
start-process "C:\Program Files\Common Files\microsoft shared\ClickToRun\OfficeC2RClient.exe" -ArgumentList "/update user"cd "C:\Program Files\Common Files\microsoft shared\ClickToRun\"
.\OfficeC2RClient.exe /update userRepair Word-Registry
use when Word does not start or crash on start
This will not repair the Word, but may fix issues with the Windows-Registry. Only works with Word…
winword.exe /rOffice 365 EXE names:
| Word | winword.exe |
| Excel | excel.exe |
| PowerPoint | powerpnt.exe |
| Outlook | outlook.exe |
| OneNote | onenote.exe |
| Access | msaccess.exe |
Outlook
Outlook switches
| Safe Mode | outlook.exe /safe |
| Clean Views | outlook.exe /cleanviews |
| Profile Prompt | outlook.exe /profiles |
| Clean Rules use when the Rules-Button in File>Account-Settings>Deligate-Access throws an error /cleanrules removes all rules on client and server! | |
| delete Rules on Client | outlook.exe /cleanclientrules |
| delete Rules on Server | outlook.exe /cleanserverrules |
| delete All Rules | outlook.exe /cleanrules |
Other Oultook Switches
| reset Folder Names | outlook.exe /ResetFolderNames |
| reset Folders | outlook.exe /ResetFolders |
| reset Ribbon | outlook.exe /ResetOutlookBar |
| reset Navigation | outlook.exe /ResetNavPane |
| clear ItemProcSearch1 | outlook.exe /cleanips |
- Clears the ItemProcSearch Folder, when messages are stuck in the item processing pipeline (e.g. Outbox-Queue) ↩︎
SCCM
Clear CCM-Cache
Remove-Item -Recurse -Force -ea SilentlyContinue "C:\Windows\ccmcache\*"Repair SCCM (local)
Log-Location: C:\Windows\ccmsetup\Logs\ccmsetup.log
Setup will end in CcmSetup is exiting with return code #
# = 0 -> Setup Successful
# = 7 -> Restart Required (will continue/finalize repair/install after the restart)
Any other value is usually an error and needs investigation
Start-Process -Wait C:\Windows\CCM\ccmrepair.execd %WinDir%\CCM\
.\ccmrepair.exeSCCM – Repair (remote)
function SCCM-RepairClient([String] $CompName) {
$SCCMClient = [wmiclass] "\\$CompName\root\ccm:sms_client"
$SCCMClient.RepairClient()
}
$ComputerName=Read-Host "`r`nSCCM-Client Repair:`r`n-------------------`r`nEnter Computername"
SCCM-RepairClient -ComputerName "$ComputerName"Un-install SCCM
Log-Location: Same as in repair above
Start-Process -Wait "C:\Windows\CCMSetup\CCMSetup.exe" -ArgumentList "/uninstall"Re-Install SCCM
Site-Code = 3-character code to specify the SCCM-Site, such as AA0, CXX, P01
If no site code is provided, SCCM will automatically search in the network and use the first one found
Log-Location: Same as in repair above
Read-Host "Enter the SCCM Site-Code"
Start-Process "CCMSetup.exe" -ArgumentList "SMSSITECODE=$siteCode"Hint: in most cases this works best when done directly from the Backend via Configuration Manager console > Right-Click on Device > Install Client
(Select ‘Always install the Client Software’, ‘Uninstall existing …’ & ‘Install the Client Software form a specified Site’)
Start SCCM Client Actions
$SCCMActions = @{
"Hardware Inventory Cycle" = "{00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000001}"
"Software Inventory Cycle" = "{00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000002}"
"Discovery Data Collection Cycle" = "{00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000003}"
"File Collection Cycle" = "{00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000010}"
"Machine Policy Retrieval & Evaluation Cycle" = "{00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000021}"
"Software Metering Usage Report Cycle" = "{00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000031}"
"Windows Installer Source List Update Cycle" = "{00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000032}"
"Software Updates Scan Cycle" = "{00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000113}"
"Software Updates Deployment Evaluation Cycle" = "{00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000108}"
"Application Deployment Evaluation Cycle" = "{00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000121}"
}
foreach ($Action in $SCCMActions.GetEnumerator()) {
Write-Host "Running: $($Action.Key)"
Invoke-WmiMethod -Namespace "root\ccm" -Class SMS_Client -Name TriggerSchedule -ArgumentList $Action.Value | Out-Null
}
Write-Host "All SCCM Client Actions triggered."Automated Repair (incl. Scans and reset)
# Restart SCCM Client Service
Write-Host "Restarting SCCM Service..."
Restart-Service CcmExec -Force -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
Start-Sleep -Seconds 10
# Run SCCM Client Repair
Write-Host "Running SCCM Client Repair..."
Start-Process "C:\Windows\CCM\ccmrepair.exe" -Wait -ErrorAction Stop -NoNewWindow
# Print Repair Result
$ccmSetupLogFolder = "C:\Windows\ccmsetup\Logs"
$ccmsetupLogFile="ccmsetup.log"
if (Test-Path $ccmsetupLogFolder\$ccmsetupLogFile) {
$logLines = Get-Content -Path $ccmsetupLogFolder\$ccmsetupLogFile -Tail 3
foreach ($line in $logLines) {
if ($line -match "<!\[LOG\[(.*?)\]LOG\]!>") {
$logMessage = $matches[1]
# only print if logmessage starts with "CcmSetup is exiting with return code"
if ($logMessage -like "CcmSetup is exiting with return code*" -or $logMessage -like "CcmSetup failed with error code*") {
Write-Host "Log Message: $logMessage"
}
}
}
}
# Clear SCCM Cache
Write-Host "Clearing SCCM Cache..."
$CachePath = "C:\Windows\ccmcache\*"
If (Test-Path $CachePath) {
Remove-Item $CachePath -Recurse -Force -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
}
# Trigger SCCM Cycles
Write-Host "Triggering SCCM Client Actions..."
$Schedules = @(
"{00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000021}", # Machine Policy Retrieval
"{00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000022}", # Machine Policy Evaluation
"{00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000113}", # Software Update Scan
"{00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000108}", # Software Update Deployment Eval
"{00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000121}" # Application Deployment Eval
)
foreach ($Schedule in $Schedules) {
Invoke-WmiMethod -Namespace "root\ccm" -Class SMS_Client -Name TriggerSchedule -ArgumentList $Schedule | Out-Null
}
Write-Host "Restarting Software Center..."
Stop-Process -Name SCClient -Force -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
Start-Process "C:\Windows\CCM\ClientUX\SCClient.exe"Uninstall SCCM
Start-Process -FilePath "C:\Windows\CCMSetup\ccmsetup.exe" -ArgumentList"/uninstall" -Wait -ErrorAction Stop -NoNewWindowModern Apps
MS-Teams
Cache Location:
%LOCALAPPDATA%\Packages\MSTeams_8wekyb3d8bbwe\LocalCacheOneDrive Reset
To reset the current sync profile and cache run the following:
C:\Program Files\Microsoft OneDrive\OneDrive.exe /resetActive Directory
Search User by PhoneNr
$number = Read-Host -Prompt "What is the mobile phone number you are looking for"
Write-Host "`r`nStarting Search.`r`nProcess will stop if a match is found.`r`nTo cancel Press 'Ctrl+C'."
$number = $number -replace '[^0-9]' # Normalize input
$match = Get-ADUser -Filter * -Properties MobilePhone, HomePhone, OfficePhone, DisplayName, sAMAccountName |
Select-Object DisplayName, sAMAccountName, MobilePhone, OfficePhone, HomePhone |
Where-Object {
($_.MobilePhone -replace '[^0-9]' -like "*$number*") -or
($_.OfficePhone -replace '[^0-9]' -like "*$number*") -or
($_.HomePhone -replace '[^0-9]' -like "*$number*")
} | Select-Object -First 1
if ($match) {
Write-Host "`r`nMatch found:`r`n$match"
} else {
Write-Host "`r`nNo match found."
}List all Groups, a user is member of
$user=read-host "enter username"
((Get-ADUser $user -Properties MemberOf ).MemberOf.split(",")| where-object {$_.contains("CN=")}).replace("CN=","")Add a User to a Group
$user=read-host "enter username"
$adGroup=Read-Host "Enter User-Group name"
Add-ADGroupMember -Identity $adGroup -Members $userCompare Usergroup Membership
Compares 2 users and lists the ‘Member of’-Groups that are missing on User1
$user1=read-host "enter username User1"
$user2=read-host "enter username User2"
$users = $user1, $user2
$user1Groups = ((Get-ADUser $users[0] -Properties MemberOf).MemberOf.split(",") | where-object { $_.contains("CN=") }).replace("CN=", "")
$user2Groups = ((Get-ADUser $users[1] -Properties MemberOf).MemberOf.split(",") | where-object { $_.contains("CN=") }).replace("CN=", "")
$missingInUser1 = $user2Groups | Where-Object { $user1Groups -notcontains $_ }
Write-Host "`r`n`r`n`r`nFollowing groups are missing for $user1 :"
$missingInUser1list Goups in a specific OU
with $searchBase specify the path in reverse order.
if the OU location is part of company.com then enter: OU=location,OU=company.com
$searchBase=read-host "enter OU path in reverse Order"
Get-ADObject -Filter 'objectClass -eq "group"' -SearchBase $searchBase -Properties DistinguishedName, ManagedBy, Description | ForEach-Object {
$groupCN = $_.DistinguishedName.split(",") | Where-Object { $_.contains("CN=") } | ForEach-Object { $_.replace("CN=", "") }
$owner = if ($_.ManagedBy) { (Get-ADUser -Identity $_.ManagedBy).SamAccountName } else { "No owner" }
[PSCustomObject]@{
GroupCN = $groupCN
Description = $_.Description
Owner = $owner
}
} | Group-Object Owner | ForEach-Object {
Write-Output "Owner: $($_.Name)"
$_.Group | ForEach-Object {
Write-Output " - Group: $($_.GroupCN)"
Write-Output "Path: $($_.Description)"
Write-Output ""
}
Write-Output ""
}Network commands
Network Configuration Info
ipconfig /allTest TCP Connection
Test-NetConnection -RemoteAddress example.com -RemotePort 443renew DNS
ipconfig /flushdns
ipconfig /registerdnsrenew IP (dhcp)
ipconfig /release
ipconfig /renewIP/Hostname resolve
resolves Hostname/Webdomain to its IP address and vice versa
additionally shows the resolving Nameserver that handled the request
nslookup <hostname/domain/IP-Address>Follow request path
lists the ip-Adresses of DevicesServers that handle your request
tracert <domain/IP-Address>list devices in local Network
lists the known MAC-Adresses of Devices in the local Network with the dedicated IP-Address
arp -aWho Is
shows the ‘WhoIs’ information (owner-information)of a domain
whois <domain>Info
Official Domains (eg. microsoft.com) have the WhoIs information public.
This information may indicate that a mail/Website might be malicious
Attention: the WhoIs information is provided by the Domain-Owner. Therefore it may be false!
WhoIs Information may indicate a malicous domain, but never that it is save!
WhoIs Information may be redacted for privacy reasons. This may be for ‘save’ private Domains and malicous ones!
WhoIs is not part of windows 10 and upwards
download from Microsoft SysInternals | WhoIs
either copy whois.exe to C:\Windows\system32\ or go to the whois.exe-location in CMD by entering cd <Directory-Path-to-whois.exe>
show known Networks
netsh wlan show profilesshow Wifi Interfaces
netsh wlan show interfacesChange Wifi Priority
netsh wlan set profileorder name="NETWORK-PROFILE-NAME" interface="YOUR-INTERFACE-NAME" priority=1connect to Remote PowerShell
Enter-PSSession -ComputerName <remote-ComputerName>Port-Scans:
Scan for open TCP-Ports
mkdir -force C:\_temp
Get-NetTCPConnection -State Established | Tee-Object -file C:\_temp\tcp_all.logScan for open UDP-Ports
mkdir -force C:\_temp
Get-NetUDPEndpoint | Tee-Object -file C:\_temp\udp_all.logScan for specific Ports
To Search UDP-Ports used for a specific IP, change -LocalPort to -LocalAddress
mkdir -force C:\_temp
$port= Read-Host "Enter the Port-Number"
Get-NetUDPEndpoint -LocalPort $port | Select-Object LocalAddress,LocalPort,OwningProcess,@{
Name="ProcessName"
Expression={((Get-Process -Id $_.OwningProcess).Name )}
} | Tee-Object -file "C:\_temp\udp_$port.log"new Windows Profile
Automated
Download the Script from Github: removeUserProfile.ps1
(e.g. move to C:\Temp\ )
or directly download it into the Temp Folder using Powershell:
Invoke-WebRequest -Uri "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/halatsWol/PowerShell-Tools/main/scripts/removeUserProfile.ps1" -OutFile "C:\Temp\removeUserProfile.ps1"- Restart Device & Log in as different user (Admin)
- open Powershell as Administrator
- Navigate to the Folder where the Script is located using
cd C:\Temp\ - (optional) bypass Script-Execution (confirm with ‘Y’):
Set-ExecutionPolicy Bypass- Execute the Script
.\removeUserProfile.ps1- enter the Username of the Account to be cleaned up
- Restart the device
- let the User sign in with their Account
- All exports of the Cleanup are located in C:\_IT-ProfileCleanup\
Network-Drives can be remapped runningNetDrives_<UserName>.cmd
installed Printers are listed inPrinterList_<UserName>.txt - copy relevent data from old profile to new profile-Folder (Documents, Pictures, etc. … if they are not synced via OneDrive or similar)
Manual
- whith the user still signed in, make a Screenshot of the Mapped Network-Drives and Printers
- Restart Device & Log in as different user (Admin)
- open the following path:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\ProfileList- here you will find at least one Key (Folder) named something like S-1-5-21-3552239657-3581867678-65225843-1001
look through the Keys in ProfileList and look in each under ProfileImagePath for the User - get the Name of the Key (=SID) and copy it aside (e.g. into Editor)
- go right-click in the Registry on the Key > Export
- delete the SID-Key in ProfileList (the whole folder)
- (only if available) in HKEY_USERS look again for the Keys containing the SID-Key (also the one ending in <SID-Key>_classes)
select each Key, go to in the Registry Window > File & click on Unload Hive… - In Explorer: rename User folder C:\Users\<username> to C:\Users\<username>.OLD
- Restart the device
- let user Login again
- set up printer, network Drives etc
- copy relevent data from old profile to new profile-Folder (Documents, Pictures, etc. … if they are not synced via OneDrive or similar)
- delete old profile Folder
following directories may be relevant to copy from old Profile:
only copy if they are not (part of) the reason why a new Profile has been created
- Sticky-Notes:
C:\Users\<UserName>\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Sticky Notes - WSL:
in the following path: C:\Users\<UserName>\AppData\Local\Packages\
WSL will be stored in folders depending on the OS used…
e.g. Ubuntu will be in a Folder named something like CanonicalGroupLimited.Ubuntu22.04LTS_79rhkp1fndgsc\
DISM Install Features
Get all features
dism /online /get-features /format:tableInstall feature
if output says Pending, a reboot is needed
$feature = Read-Host "Enter the Feature Name"
Dism /online /Enable-Feature /FeatureName:$feature /norestart /quiet
Dism /online /Get-FeatureInfo /FeatureName:$featureset /p feature=Enter the Feature Name:
Dism /online /Enable-Feature /FeatureName:%feature% /norestart /quiet
Dism /online /Get-FeatureInfo /FeatureName:%feature%Disable feature
if output says Pending, a reboot is needed
$feature = Read-Host "Enter the Feature Name"
Dism /online /Disable-Feature /FeatureName:$feature /norestart /quiet
Dism /online /Get-FeatureInfo /FeatureName:$featureset /p feature=Enter the Feature Name:
Dism /online /Disable-Feature /FeatureName:%feature% /norestart /quiet
Dism /online /Get-FeatureInfo /FeatureName:%feature%Specific Features and Capabilities
XPS-Viewer
dism /Online /Add-Capability /CapabilityName:XPS.Viewer~~~~0.0.1.0Windows Tools
Windows Tools
Run Win+R to Execute
| Icon | Executable | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| cleanmgr.exe | Disk Cleanup Manager | Removes unnecessary files from your hard drive | |
| compmgmt.msc | Computer Management | Provides a centralized console for managing system components. | |
| control.exe | Control Panel | a central hub for system settings | |
| control.exe keymgr.dll | Credential Manager | Manage stored Login Credetials | |
| control.exe smscfgrc | SCCM Configruation Manager Properties | clear Cache, Trigger Scans and read properties of Configuration Manager | |
| desk.cpl | Display Settings (new) | Set up and customize Display Resolution, Position, etc. | |
| devmgmt.msc | Device Manager | Manages hardware devices | |
| diskmgmt.msc | Disk Management | for managing disk partitions and volumes. | |
| dxdiag.exe | DirectX Diagnostic Tool | Diagnoses DirectX-related issues and provides system information. | |
| eventvwr.msc | Event Viewer | Logs system events, errors, and warnings | |
| gpedit.msc | Group Policy Editor | Configures group policies | |
| gpedit.msc /gpcomputer: RemoteDevice | Group Policy Editor (remote) | Configures group policies on a remote device, current user (or user running shell/commandline) requires Admin permissions on the remote device | |
| inetcpl.cpl | Internet Properties | Configures Internet Explorer settings | |
| intl.cpl | Region | Win95 Region and Format Settings | |
| lusrmgr.msc | Local Users and Groups | Manages local user accounts and groups | |
| mdsched.exe | Memory Diagnostic Scheduler | Diagnoses memory issues | |
| mmc.exe | Microsoft Management Console | A framework for managing various system components | |
| mmsys.cpl | Multimedia Control Panel | for configuring audio and video devices. | |
| msconfig.exe | System Configuration | Configures system startup settings | |
| msdt.exe | Diagnostic tool | used for various hardware and software troubleshooting. | |
| msinfo32.exe | System Information | Provides detailed information about system hardware and software | |
| ncpa.cpl | Network Connections (Network Adapters) | Folder for all network Adapters, used for Adapter-specific Network-Configuration | |
| netstat.exe | Network Statistics | for viewing network connections and statistics (CMD Tool). | |
| perfmon.exe | Performance Monitor | Monitors system performance metrics | |
| perfmon.exe /rel | Reliability Monitor | Tracks system reliability and helps identify and resolve common issues. | |
| regedit.exe | Registry Editor | for editing the Windows Registry | |
| resmon.exe | Resource Monitor | Provides a real-time view of system resource usage, including CPU, memory, disk, and network activity | |
| secpol.msc | Local Security Policy | Configures security settings | |
| services.msc | Services | for managing system services | |
| sysdm.cpl | System Properties | Provides system information and settings | |
| taskmgr.exe | Task Manager | for monitoring system performance and processes | |
| taskschd.msc | Task Scheduler | for managing planned and reoccurring Tasks | |
| timedate.cpl | Date and Time | Win95 Date and Time Settings | |
| winver.exe | Windows Version | Displays Windows version and build information. |
Alphabet
English
A Alpha | B Beta | C Ceasar | D Delta | E Echo |
F Foxtrott | G Golf | H Hotel | I India | J Juliet |
K Kilo | L Lima | M Mike | N November | O Oscar |
P Papa | Q Quebec | R Romeo | S Sierra | T Tango |
U Uniform | V Victor | W Whiskey | X X-Ray | Y Yankee |
Z Zulu |
|
|
|
|
German
A Anton | B Berta | C Cäsar | D Dora | E Emil |
F Friedrich | G Gustav | H Heinrich | I Ida | J Julius |
K Konrad | L Ludwig | M Marta | N Nordpol | O Otto |
P Paula | Q Quelle | R Richard | S Siegfried | Sch Schule |
T Theotor | U Ulrich | V Viktor | W Wilhelm | X Xaver |
Y Ypsilon | Z Zeppelin | Ä Ärger | Ö Ökonom | Ü Übermut |